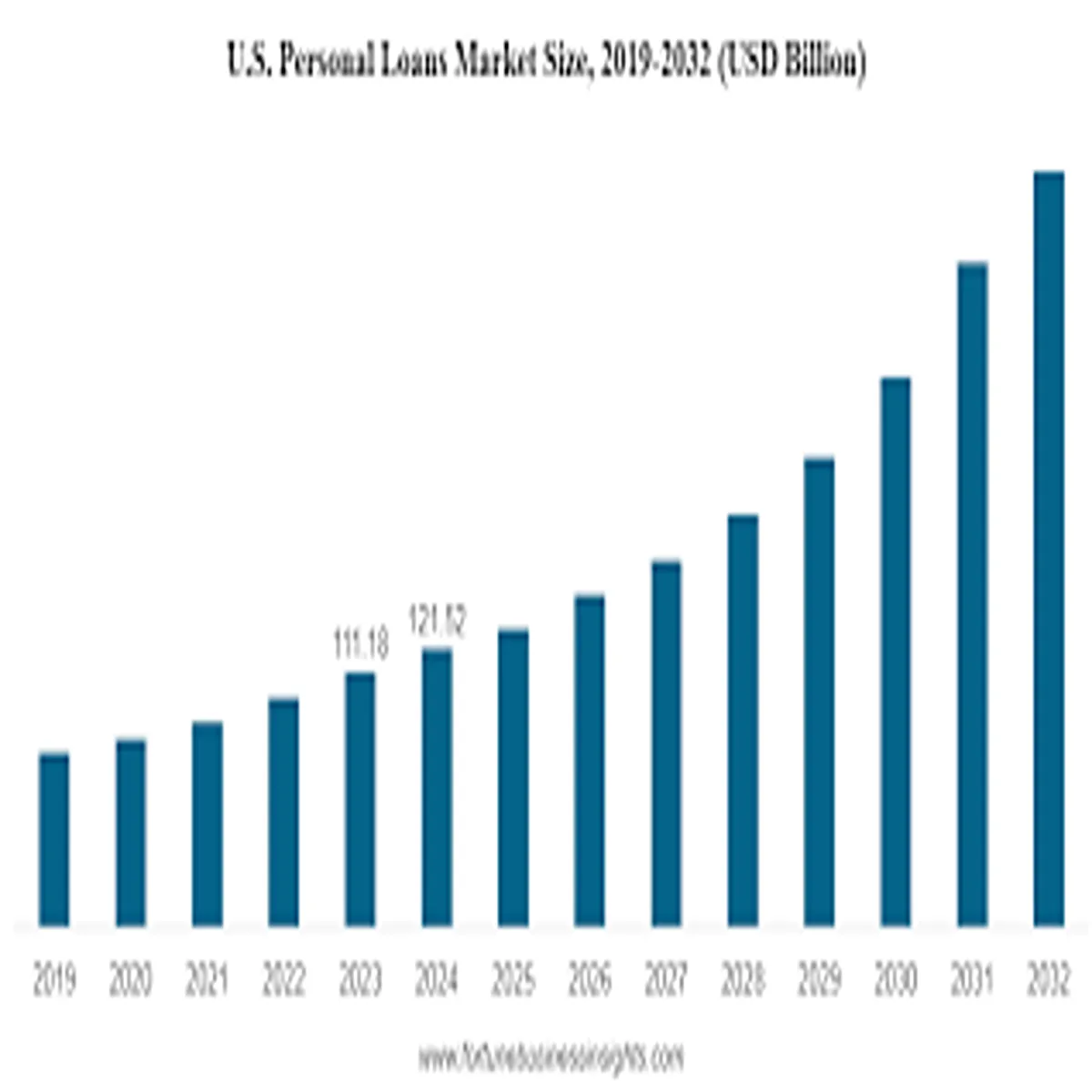
U.S. Loan Market 2026- The U.S. loan market is entering 2026 with cautious optimism as interest rates stabilize, inflation cools, and consumer demand shows signs of resilience. From mortgages and auto loans to personal loans and small business financing, borrowing trends across the country reflect a shifting economic landscape. Data from federal agencies and leading financial institutions suggest that while credit remains widely available, Americans are becoming more selective—and lenders more disciplined—after two years of higher borrowing costs.
Mortgage Rates Show Signs of Stabilizing
After peaking during the Federal Reserve’s aggressive tightening cycle in 2022–2023, mortgage rates have gradually eased but remain above pre-pandemic lows. According to recent market averages, 30-year fixed mortgage rates are hovering in the mid-to-high 6% range, compared to historic lows near 3% in 2021.
Housing economists note that affordability remains a challenge, particularly for first-time buyers. While home prices in many metropolitan areas have moderated, they have not declined significantly enough to offset elevated interest costs. The Federal Reserve has indicated that any further rate cuts will depend on sustained evidence of inflation returning toward its 2% target, meaning mortgage rates are unlikely to fall sharply in the short term.
For prospective buyers, this environment has led to increased demand for adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) and rate buydown programs. Lenders are also reporting stronger interest in refinancing among borrowers who purchased homes at higher rates in 2023 and 2024.
Auto Loans: Higher Costs Reshape Consumer Choices
Auto loan rates remain elevated compared to pre-2022 levels, reflecting broader credit conditions. Average new car loan rates are currently above 7%, with used vehicle financing often exceeding 9%, depending on credit profile.
Data from the Federal Reserve Bank of New York show that auto loan balances continue to grow, but delinquency rates—particularly among subprime borrowers—have ticked up modestly over the past year. Analysts say rising insurance premiums and higher vehicle prices have added pressure to household budgets.
In response, consumers are opting for longer loan terms, leasing options, and more fuel-efficient models. Electric vehicle financing programs, supported by federal incentives under legislation such as the Inflation Reduction Act, have also influenced buyer behavior, particularly in states with additional rebates.
Personal Loans Gain Popularity for Debt Consolidation
As credit card interest rates remain near record highs—often exceeding 20% APR—many Americans are turning to personal loans for debt consolidation. Fixed-rate personal loans offer borrowers a structured repayment schedule and, in some cases, lower interest rates than revolving credit.
Major banks and online lenders report steady growth in unsecured personal loan originations. However, underwriting standards have tightened slightly, especially for applicants with lower credit scores. Financial advisors emphasize the importance of reviewing total repayment costs, fees, and prepayment penalties before consolidating debt.
Recent surveys indicate that borrowers are increasingly using personal loans not only for credit card refinancing but also for home improvements and emergency expenses. The trend reflects a broader effort by households to manage cash flow amid persistent living costs.
Student Loan Repayment Resumes Full Impact
The resumption of federal student loan payments has had a measurable effect on household finances. After pandemic-era payment pauses ended, millions of borrowers re-entered repayment plans. The U.S. Department of Education introduced income-driven repayment adjustments aimed at easing the transition.
While widespread default spikes have not materialized, analysts warn that repayment obligations are reducing discretionary spending, particularly among younger consumers. Some borrowers are exploring refinancing options with private lenders, though this typically means giving up federal protections such as income-driven plans and potential forgiveness programs.
Policy discussions around student debt relief remain active in Washington, but no broad-based cancellation program is currently in effect.
Small Business Lending Sees Cautious Recovery
Small business lending activity slowed during periods of higher interest rates but is gradually rebounding. According to data from the U.S. Small Business Administration, loan approvals under key programs have increased modestly in recent quarters.
Banks report that business owners are borrowing primarily for equipment upgrades, technology investments, and working capital rather than aggressive expansion. Credit standards remain tighter than pre-pandemic norms, reflecting ongoing concerns about economic uncertainty.
Regional banks and credit unions continue to play a significant role in local lending markets, especially in underserved communities. Meanwhile, fintech lenders are leveraging digital underwriting tools to speed up approval times, though interest rates can vary widely based on risk profiles.
Credit Standards and Delinquency Trends to Watch
One of the most closely monitored indicators in the loan market is delinquency. Recent quarterly reports show slight increases in late payments across credit cards and auto loans, particularly among younger and lower-income borrowers. However, overall delinquency levels remain below the peaks seen during the 2008 financial crisis.
Lenders have responded by tightening credit standards in select categories. The Senior Loan Officer Opinion Survey indicates that banks are exercising greater caution in approving unsecured loans and commercial real estate financing.
At the same time, consumer credit demand remains steady. Employment levels are still relatively strong, which has supported repayment capacity for most households. Economists suggest that as long as job growth continues, widespread credit distress is unlikely.
What Borrowers Should Consider in 2026
For American consumers navigating today’s loan environment, experts recommend focusing on credit health, comparing multiple lenders, and understanding total borrowing costs. Key considerations include:
- Monitoring credit scores before applying
- Locking in fixed rates when possible
- Avoiding unnecessary long-term extensions
- Reviewing federal versus private loan protections
Digital comparison platforms have made it easier to shop for loans, but financial advisors caution against choosing solely based on advertised rates. Fees, penalties, and lender reputation should also factor into decision-making.
Outlook: Gradual Normalization, Not Rapid Decline
Looking ahead, most analysts expect a gradual normalization of interest rates rather than a sharp drop. The direction of Federal Reserve policy, inflation data, and labor market performance will remain central to the loan market’s trajectory.
For now, the U.S. credit system appears stable but more disciplined. Borrowers are adjusting to a “higher-for-longer” rate environment, while lenders balance growth opportunities with prudent risk management.
As 2026 unfolds, the loan market will likely continue reflecting broader economic signals—steady, cautious, and closely watched by consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike.