US Insurance Market in 2026- The U.S. insurance market is entering 2026 with significant shifts that are directly affecting households, small businesses, and investors. From rising home and auto insurance premiums to tighter underwriting standards and increased regulatory scrutiny, the industry is navigating inflation pressures, climate risks, and rapid digital transformation. Recent data from federal agencies and industry groups show that while insurers are stabilizing profitability after several volatile years, consumers in many states are paying more for coverage and reassessing how much protection they truly need.
Auto Insurance Rates Continue to Climb Nationwide
Auto insurance remains one of the most searched insurance topics across Google Search and Google Discover in the United States—and for good reason. According to recent consumer price data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, motor vehicle insurance costs increased sharply over the past year, reflecting higher repair costs, medical claims, and vehicle prices.
Industry analysts point to multiple drivers behind the surge:
- Elevated labor and parts costs for vehicle repairs
- Increased frequency of severe accidents
- Rising medical expenses tied to claims
- Growth in uninsured and underinsured drivers
Insurers have filed for rate adjustments in numerous states, with regulators in places like California and Florida reviewing double-digit percentage increases. While some rate hikes are slowing compared to peak levels seen in 2023 and 2024, premiums remain elevated relative to pre-pandemic levels.
For consumers, comparison shopping and usage-based insurance programs—often marketed as telematics or safe-driving discounts—are becoming more common strategies to manage costs.
Home Insurance Under Pressure From Climate Risk
Homeowners insurance is also undergoing structural change, particularly in disaster-prone regions. Wildfires in the West, hurricanes along the Gulf Coast, and severe storms across the Midwest have led to record insured losses over the past several years.
Data compiled by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners shows that insurers are tightening underwriting standards in high-risk ZIP codes. In certain areas, carriers have reduced new policy issuance or increased deductibles for wind, hail, or wildfire coverage.
States including Florida and California have implemented regulatory reforms to stabilize their insurance markets. In Florida, legislative changes aim to reduce litigation costs and attract more insurers back into the state. In California, regulators are working to modernize rate-setting rules to reflect catastrophe modeling and reinsurance costs more accurately.
For homeowners, this means:
- Higher premiums in high-risk regions
- Increased scrutiny during policy renewals
- Greater demand for mitigation measures like fortified roofs and fire-resistant landscaping
Insurance availability—not just price—has become a central issue in local housing markets.
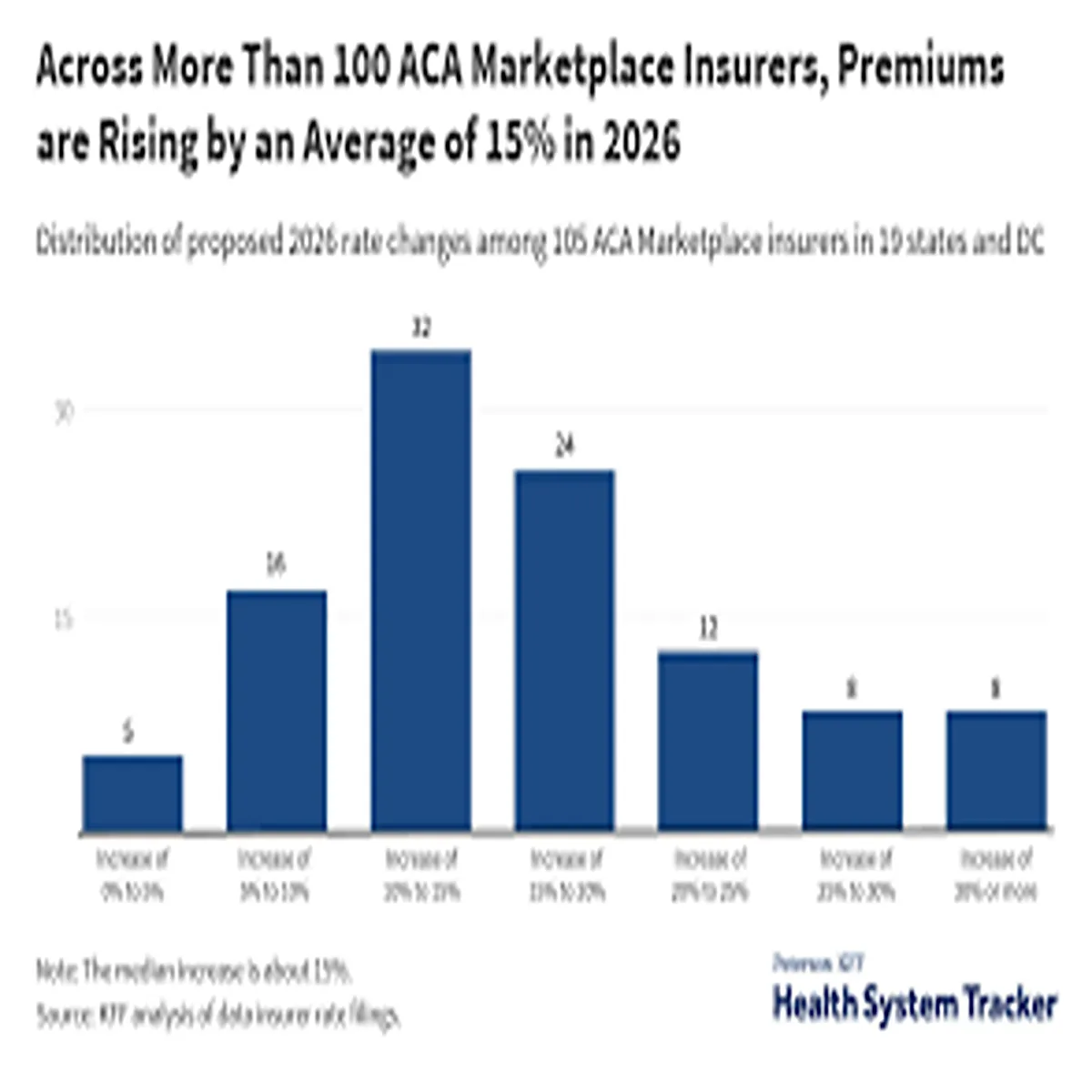
Health Insurance Premium Trends in 2026
Health insurance remains a dominant concern for American families. Enrollment through the Affordable Care Act marketplaces has reached record levels in recent years, supported by enhanced federal subsidies extended through the Inflation Reduction Act.
While benchmark premiums have seen moderate changes in many states, out-of-pocket costs, provider network limitations, and prescription drug pricing continue to shape consumer decisions. Insurers are also investing more heavily in digital care management, telehealth platforms, and value-based payment models.
Employer-sponsored health insurance, which covers the majority of working Americans, is also evolving. Employers are increasingly exploring:
- High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) paired with Health Savings Accounts
- Tiered provider networks
- Wellness incentives tied to premium reductions
The broader goal is cost control without sacrificing access—though employees often face higher deductibles and more plan complexity.
Insurance Companies Turn to AI and Automation
Digital transformation is accelerating across the insurance sector. Major carriers are investing in artificial intelligence tools for claims processing, fraud detection, and underwriting efficiency. According to industry disclosures and earnings calls, automation is reducing claims cycle times and improving customer service responsiveness.
At the same time, regulators are closely monitoring how algorithms are used in pricing decisions. State insurance departments have emphasized transparency and fairness, especially when non-traditional data sources are involved.
Consumers are seeing more mobile-first experiences:
- Instant policy quotes online
- Real-time claims tracking
- AI-assisted customer support
While technology improves convenience, privacy advocates continue to call for clear disclosure about data usage and risk scoring practices.
Reinsurance Costs and Global Market Impact
Behind the scenes, reinsurance—insurance for insurance companies—has played a major role in shaping U.S. premium trends. Following multiple years of heavy catastrophe losses worldwide, global reinsurance rates increased significantly.
Higher reinsurance costs often translate into higher premiums for policyholders, especially in property insurance. U.S. insurers have adjusted coverage terms, increased deductibles, or limited exposure in certain markets to manage capital risk.
Financial analysts note that insurer balance sheets have strengthened compared to the immediate post-pandemic period, but capital discipline remains a priority. Rating agencies continue to evaluate carriers based on catastrophe exposure, underwriting margins, and investment income performance.
Consumer Protection and Regulatory Oversight
Insurance regulation in the United States operates primarily at the state level. State insurance commissioners are reviewing rate filings, solvency standards, and market conduct practices.
In 2026, key regulatory themes include:
- Climate risk disclosure requirements
- Transparency in algorithmic underwriting
- Protection against unfair claims practices
- Strengthening insurer solvency monitoring
Consumer advocacy groups are urging regulators to balance insurer profitability with affordability concerns, particularly in vulnerable communities.
What This Means for American Households
For U.S. consumers, the insurance landscape is more complex than it was five years ago. Premium increases in auto and home insurance are pressuring household budgets, while health insurance choices remain nuanced and policy-driven.
Experts recommend that consumers:
- Review coverage limits annually
- Compare quotes from multiple carriers
- Evaluate deductibles versus premium trade-offs
- Ask about discounts, bundling options, and mitigation credits
Insurance remains a cornerstone of financial stability, but in 2026 it requires more active management from policyholders.
Outlook: Stabilization With Ongoing Volatility
Looking ahead, analysts expect gradual stabilization in some insurance lines, particularly auto insurance, as supply chains normalize and inflation moderates. However, climate-related losses, medical cost trends, and regulatory changes will continue shaping the market.
For investors, insurers remain sensitive to interest rate movements and catastrophe exposure. For consumers, transparency, comparison shopping, and financial literacy are becoming essential tools.
The U.S. insurance market is not in crisis—but it is clearly in transition. And for millions of Americans, the cost and structure of coverage will remain a central financial issue throughout 2026.